States with illnesses: Arizona 5, California 12, Idaho 2, Illinois 2, Kentucky 1, Massachusetts 2, Maine 1, Michigan 1, Minnesota 3, North Carolina 2, New Jersey 1, Ohio 1, Oregon 4, Pennsylvania 1, Rhode Island 1, Texas 8, Virginia 1, Washington 2 and Wisconsin 1.
Illnesses occurred from December 2023 through December 2025.
ByHeart infant formula was distributed to Argentina, Brazil, Brunei, Canada, Chile, China, Colombia, Ecuador, Egypt, Hong Kong, Israel, Jamaica, Japan, Republic of Korea, Peru, Philippines, Romania, Singapore, South Africa, Thailand, and the British Virgin Islands.

The FDA and CDC, in collaboration with the California Department of Public Health (CDPH), Infant Botulism Treatment and Prevention Program (IBTPP), and other state and local partners, continue to investigate a multistate outbreak of infant botulism. Epidemiologic and laboratory data show that ByHeart Whole Nutrition infant formula is contaminated with Clostridium botulinum, which is causing infant illness in multiple regions of the country.
ByHeart’s and FDA’s investigations into the root cause of the outbreak are ongoing, and at this time, FDA cannot rule out the possibility that contamination might have affected all ByHeart formula products. In response, CDC broadened the case definition to include any infant with botulism who was exposed to ByHeart formula at any time since the product’s release in March 2022. As of December 10, 2025, a total of 51 infants with suspected or confirmed infant botulism and confirmed exposure to ByHeart Whole Nutrition infant formula (various lots) have been reported from 19 states.
Previously, case counts included illnesses from August 1, 2025, onward. With the expanded definition, CDC and state partners identified 10 additional cases that occurred from December 2023 through July 2025. At this time, no cases have been identified between March 2022 and December 2023. All 10 are confirmed infant botulism cases with documented exposure to ByHeart formula.
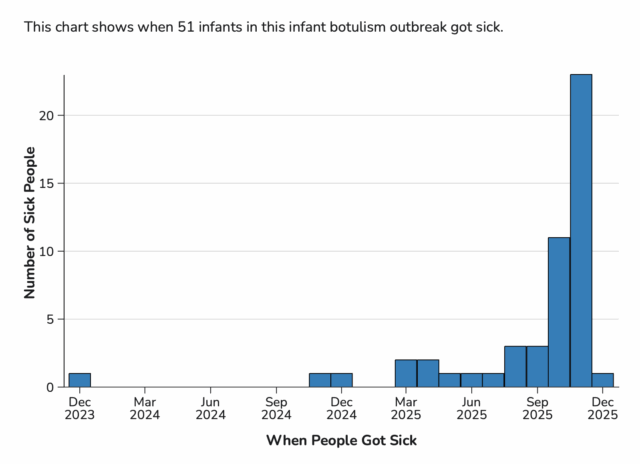
Laboratory confirmation for some cases is ongoing. Illnesses started on dates ranging from December 24, 2023 to December 1, 2025. All 51 infants were hospitalized. No deaths have been reported to date. The infants range in age from 16 to 264 days and 22 (43%) are female.
State and local public health officials are interviewing caregivers about the foods the infants were fed in the month before they got sick. Fifty-one infants have been identified that were fed ByHeart Whole Nutrition powdered infant formula before getting sick.
FDA has not received reports of recalled formula being found on store shelves since November 26, 2025. All ByHeart infant formula products have been recalled, and these products should not be available for sale in stores or online. This includes all formula cans and single-serve “anywhere pack” sticks.
Additional testing by ByHeart, FDA, CDC, and state partners is underway, and results are expected in the coming weeks. Positive sample results for finished product testing will be included and updated in the Sample Results section.
FDA’s investigation is ongoing to determine the point of contamination. This advisory will be updated as information becomes available.
Product sampling and testing is being conducted by FDA, CDC, state partners, and ByHeart. Available information on positive samples is included below. This table will be updated as additional results become available or are shared with FDA.
Due to the large number of samples, only positive results are being reported here. The detection of Clostridium botulinum in infant formula is complex, and a negative test result does not rule out the presence of the bacteria in the product.
Parents and caregivers should not use any ByHeart infant formula, regardless of test results.
| Sample Collected/Analyzed by | Product | Test Result | Toxin Type |
| CDPH | Opened container of ByHeart Infant Formula (Batch No. 251131P2) | Positive | Type A |
| ByHeart | ByHeart Infant Formula (Batch/Batches Not Reported) | Positive | Type A |
| ByHeart | ByHeart Infant Formula (Batch/Batches Not Reported) | Positive | Type A |
| ByHeart | ByHeart Infant Formula (Batch/Batches Not Reported) | Positive | Type A |
| ByHeart | ByHeart Infant Formula (Batch/Batches Not Reported) | Positive | Type A |
| ByHeart | ByHeart Infant Formula (Batch/Batches Not Reported) | Positive | Type A |
What Parents Need to Know:
What is Infant Botulism?
Infant botulism is a rare but serious condition caused by the ingestion of Clostridium botulinum spores, which can grow in the intestines of infants (typically those under one year old) and produce a potent toxin. This condition usually occurs when infants consume contaminated foods, particularly honey, which is known to harbor spores. The spores can germinate in the immature gastrointestinal tract of infants, leading to toxin production and subsequent illness.
Symptoms – What to watch for
Symptoms of infant botulism typically appear between 12 to 36 hours after ingestion of the spores and may include:
• Constipation: Often the first sign, with stools that may become less frequent and harder.
• Weakness: A general lethargy or decreased muscle tone (hypotonia), often described as “floppy baby syndrome.”
• Poor Feeding: Difficulty feeding or sucking.
• Cranial Nerve Dysfunction: This can lead to symptoms such as:
– Weak cry or inadequate vocalization.
– Difficulty swallowing.
– Drooping eyelids or poor eye movement (ptosis).
• Respiratory Problems: In severe cases, difficulty breathing due to muscle weakness can occur.
• Weakness in Movement: Reduced ability to move arms and legs.
• Irritability or unusual crying.
Treatment
Hospitalization: Infants diagnosed with botulism often require hospitalization to monitor respiratory function and general health.
Supportive Care: Treatment primarily focuses on supportive measures such as:
• Nutritional support, often via intravenous fluids or feeding tubes if necessary.
• Monitoring and management of respiratory function; in some cases, mechanical ventilation may be required if breathing difficulties arise.
• Botulism Immune Globulin (BIG): In the United States, a specific treatment called BabyBIG (Botulism Immune Globulin) is administered to infants diagnosed with botulism. This treatment helps to neutralize the Botulinum toxin and can reduce the duration and severity of symptoms.
• Antibiotics: Antibiotics are not typically used for treating infant botulism as they do not affect the toxin once produced and can also promote toxin production by encouraging the growth of bacteria.
Long-Term Prognosis
The prognosis for infants with botulism is generally good, especially with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Most infants recover fully within a few weeks or months, but the recovery time can vary.
Recovery Time: Symptoms usually resolve over several weeks, but in some cases, full recovery can take months, especially regarding muscle strength and tone.
No Long-Term Disabilities: Most children do not experience long-term complications or disabilities if treated promptly and effectively.
Follow-Up: Regular follow-ups may be necessary.
Marler Clark has been retained by 30 families whose infants consumed ByHeart formula. Some of these infants became ill in late 2024 and early to mid 2025.